 sales@loadcellsensor.com
sales@loadcellsensor.com

How to Choose the Right Torque Sensor for Your Application Needs
When it comes to selecting the right torque sensor for your specific application needs, understanding the complexities of torque measurements is crucial. Leading expert in the torque sensor industry, Dr. Emily Johnson, emphasizes that "the right torque sensor not only ensures precise measurements but also enhances the overall efficiency of your operations." This statement underlines the importance of choosing a sensor that operates seamlessly within the operational parameters of your machinery or project.
In various industries—from automotive to robotics—the demands for accurate torque measurements continue to escalate. A well-chosen torque sensor can significantly impact the performance, safety, and reliability of equipment. However, with a plethora of options available in the market today, determining the most suitable torque sensor can be daunting. Factors such as measurement range, sensitivity, size, and environmental conditions play pivotal roles in this decision-making process.
Selecting the appropriate torque sensor involves a careful analysis of your application requirements and understanding the specific characteristics of different sensors. By taking the time to evaluate these components, industries can ensure optimal performance and longevity in their machinery, validating Dr. Johnson's assertion that the right equipment paves the way for innovation and success.

Understanding Torque Sensors: Types and Applications
Torque sensors are essential tools in various industries, designed to measure the torque produced by motors and other rotating devices. Understanding the different types of torque sensors is crucial for selecting the right one for specific applications. There are primarily two types of torque sensors: contact and non-contact. Contact torque sensors measure torque by direct interaction with the rotating element, providing accurate readings in real-time. Non-contact torque sensors, on the other hand, utilize magnetic or optical methods to gauge torque without physical contact. This results in less wear and tear, making them suitable for high-speed applications where precision is paramount.
Applications of torque sensors span multiple fields, including automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and robotics. In automotive engineering, torque sensors are used to optimize engine performance and enhance fuel efficiency by providing real-time feedback on power output. In aerospace, these sensors play a critical role in testing and maintenance, ensuring that critical systems operate within safe torque limits. Meanwhile, in manufacturing, torque sensors help in quality control, ensuring that assembly processes meet specified torque values for components. In robotics, accurate torque measurement enables precise control of robotic joints, contributing to improved functionality and safety. By understanding the types and applications of torque sensors, industries can choose the most appropriate sensor to meet their specific needs effectively.
How to Choose the Right Torque Sensor for Your Application Needs
| Sensor Type | Measuring Range (Nm) | Accuracy (%) | Application Area | Typical Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static Torque Sensors | 0-500 | ±0.5 | Automotive Testing | High stability, compact design |
| Rotary Torque Sensors | 0-1000 | ±1.0 | Industrial Machinery | Wireless options, IP65 rated |
| Dynamic Torque Sensors | 0-200 | ±0.5 | Research and Development | Real-time data acquisition, high bandwidth |
| Miniature Torque Sensors | 0-50 | ±1.0 | Robotics and Automation | Compact size, low power consumption |
| Reaction Torque Sensors | 0-300 | ±0.25 | Biomedical Applications | Custom calibration, high precision |
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Torque Sensors
When selecting the right torque sensor for your application, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and accuracy. First, it’s important to assess the measurement range required for your specific application. Different torque sensors are designed to handle varying levels of torque, so understanding the expected forces involved is crucial. Additionally, the type of mechanical coupling, whether static or rotating, can significantly influence the choice of sensor, as some are more suited for particular configurations.
Another essential factor is the sensor's output type and communication protocol. Depending on the system integration requirements, you may need a torque sensor that provides analog output, digital signals, or even wireless communication options. Aligning the sensor's output capabilities with your system requirements will facilitate smoother data acquisition and analysis. Lastly, environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to chemicals should guide your decision, as certain sensors may be more robust or suitable for harsh environments, ensuring longevity and reliability in data collection.
Torque Sensor Load Capacity Comparison
Evaluating Sensor Specifications for Your Unique Needs
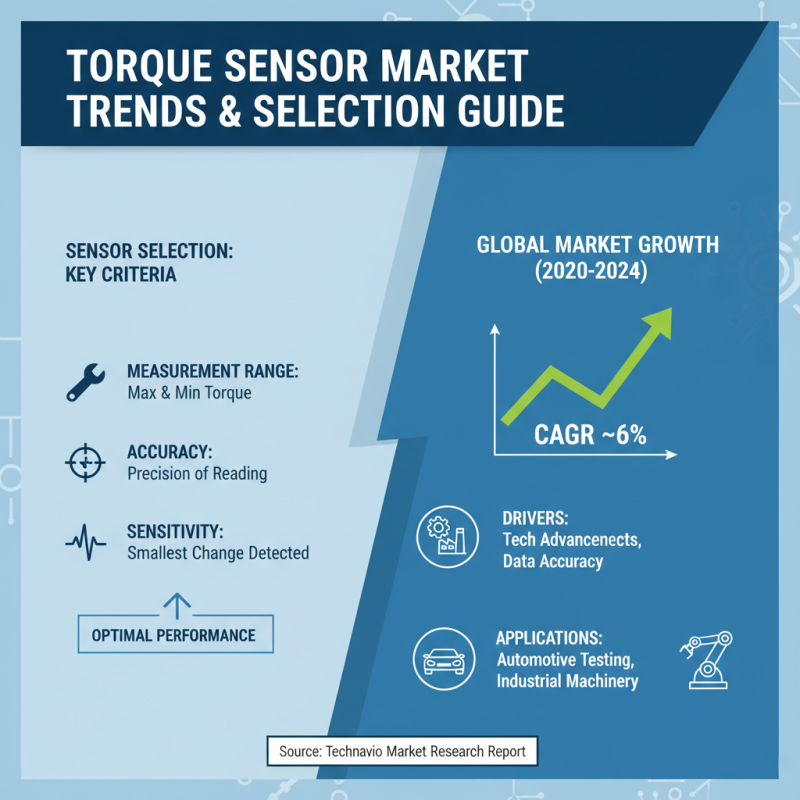
When selecting a torque sensor for specific applications, a thorough evaluation of sensor specifications is crucial to ensure optimal performance. Torque sensors vary in their measurement ranges, accuracy, and sensitivity. According to a market research report by Technavio, the global torque sensor market is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 6% from 2020 to 2024, underscoring the increasing demand for precise torque measurement across various industries. This growth is primarily driven by advancements in technology and the rising need for accurate data in applications ranging from automotive testing to industrial machinery.
One of the essential specifications to consider is the sensor type, whether it be a strain gauge, magnetostrictive, or optical sensor. Strain gauge sensors, commonly used in applications requiring high precision, can achieve accuracies of up to ±0.05% of full scale, making them ideal for critical tasks. Additionally, the operating environment plays a pivotal role; for instance, sensors designed for high-temperature applications or those exposed to harsh conditions must meet specific durability standards. Reports indicate that improper selection based on these variable factors can lead to significant measurement errors, affecting overall operational efficiency. Hence, aligning the technical specifications with the unique requirements of the application is paramount for success.
Installation and Calibration Guidelines for Torque Sensors
When it comes to the installation and calibration of torque sensors, several key factors must be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and accuracy. First and foremost, it is essential to carefully consider the environmental conditions where the sensor will be installed. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to contaminants can significantly affect the sensor’s operation. Ensure that the installation site is free from excessive vibrations and electromagnetic interference, which can distort readings.
Tips: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for mounting techniques specific to your torque sensor model. Using the appropriate fixtures and tools during installation will reduce the risk of causing damage or misalignment.
Calibration is another critical aspect of leveraging a torque sensor effectively. It should be done under controlled conditions using known reference standards to guarantee precision. Regular calibration checks should be scheduled, especially in high-usage environments, to maintain measurement integrity. Any discrepancies detected during calibration could indicate the need for adjustment or replacement.
Tip: Document all calibration results and adjustments meticulously. This record will assist in troubleshooting and maintaining compliance with quality assurance protocols over time.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Torque Sensor Selection

Selecting the right torque sensor for your application can be a complex task, often fraught with challenges. One common issue is determining the correct torque measurement range. If the range is too narrow, the sensor may overload or fail to capture the needed data, while an excessively broad range might result in reduced resolution and accuracy. To overcome this, it’s crucial to analyze the specific torque levels you expect in your application and select a sensor that closely matches these parameters.
Another challenge lies in the sensor's integration with existing systems. Compatibility with various data acquisition systems and the environment in which the sensor operates can affect performance. Issues such as signal interference or the physical size of the sensor can impede functionality. To address these concerns, it’s advisable to consult with engineers to ensure proper integration and conduct tests in the intended operational conditions. Seeking sensors with flexible communication outputs and compact designs can further streamline this integration process, ensuring seamless operation within your application.
Related Posts
-

Unleashing China's Manufacturing Excellence: A Deep Dive into the Best Torque Sensor Innovations
-

Navigating the Global Standards for Best Torque Sensor Imports and Exports
-

Maximizing Precision: Key Techniques for Effective Torque Sensor Implementation
-

Exploring Innovative Torque Sensor Types: Real-World Applications and Benefits
-

Understanding the Basics of Torque Sensor Functionality and Applications
-

12 Expert Tips for Maximizing Efficiency with Compression Force Sensors

