 sales@loadcellsensor.com
sales@loadcellsensor.com

What is a Load Cell Sensor and How Does it Work?
Load Cell Sensors are crucial in various industries, including manufacturing and construction. According to a recent market report, the global load cell sensor market is expected to grow at a rate of 5.6% over the next few years. These devices convert force into an electrical signal, playing an essential role in accurate weight measurement and load monitoring.
Expert Dr. Michael Reed states, "The effectiveness of a Load Cell Sensor lies in its precision." Such advanced technology enhances efficiency and safety in operations. Industries rely on these sensors for quality control and data collection. Despite their significant benefits, challenges exist. Variability in temperature can affect their accuracy.
Knowledge of the Load Cell Sensor's specifications is vital. Industries must choose the right type of sensor based on their specific needs. Understanding and addressing inherent limitations will be key to leveraging the full potential of these devices. As technology evolves, continuous improvement is essential to meet industry requirements.

What is a Load Cell Sensor: Definition and Purpose
A load cell sensor is a crucial device used to measure weight or force. It converts mechanical force into an electrical signal. This process allows for accurate weight readings in various applications, from industrial scales to medical devices. The key components include a strain gauge, which detects deformation, and an electronic circuit that processes this information.
The purpose of a load cell sensor extends beyond simple weight measurement. It helps maintain accuracy in manufacturing and testing. For example, in assembly lines, improper weight readings can lead to defective products. This highlights the importance of regular calibration and maintenance. Without proper care, the reliability of readings may decline, leading to poor decision-making.
In some cases, load cells can be sensitive to environmental factors. Temperature changes and vibrations may affect their accuracy. Users must be mindful of these challenges during installation and operation. Understanding these nuances can enhance performance and ensure optimal results.
Load Cell Sensor Data Comparison
Types of Load Cell Sensors: Strain Gauge, Hydraulic, and Pneumatic
Load cell sensors are essential in many industries. They measure weight or force by converting physical strain into an electrical signal. Three main types of load cells are common in various applications: strain gauge, hydraulic, and pneumatic.
Strain gauge load cells use resistive wire. When weight is applied, the wire stretches, changing its electrical resistance. This change is measured as a corresponding electrical signal. These sensors are precise and often used in digital scales. They can be sensitive, but environmental factors may affect their accuracy. Calibration is also crucial to maintain reliable readings.
Hydraulic load cells operate differently. They use fluid pressure to determine force. As weight is applied, fluid pressure increases in a sealed chamber. This change can be easily measured, making these sensors suitable for heavy loads. However, they may leak and require careful maintenance. Pneumatic load cells use air pressure rather than hydraulic fluid. They are often lighter and can handle dynamic loads well. Maintenance is still vital to prevent failure. Each type has merits and downsides. Careful selection is critical based on the application needs.
How Load Cells Work: Measuring Force through Electrical Resistance
Load cells are crucial in various industries for accurately measuring force. They operate on the principle of electrical resistance. When a load is applied, the cell deforms, changing its resistance. This change allows the system to compute the force exerted. A study by the International Society for Measurement states that load cells can achieve ±0.1% accuracy under ideal conditions.
The technology behind load cells involves a Wheatstone bridge circuit. This circuit helps in translating mechanical deformation into an electrical signal. Typically, the sensitivity of load cells varies between 0.2 mV/V to 3 mV/V, depending on the design and materials used. This variability raises questions about consistency across different manufacturers. Keeping track of these specs is essential for applications needing precision.
However, load cells can face challenges in the field. Temperature fluctuations can affect readings, causing potential errors. Additionally, mechanical shock can lead to misalignment. Industry reports indicate that up to 20% of failures in load cells are attributed to environmental factors. This highlights the need for rigorous testing and calibration in real-world conditions. Although load cells are widely used, ongoing refinements are necessary to ensure reliability and accuracy in diverse applications.
Key Applications of Load Cells in Industrial and Commercial Settings
Load cells play a crucial role in various industrial and commercial applications, from manufacturing to retail. According to industry reports, the global demand for load cells is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% through 2026. This growth is driven by the need for precision measurement in weight-sensitive operations.
In manufacturing, load cells are essential for ensuring product consistency. They are used in conveyor systems to monitor weights in real-time. For instance, in the food industry, accurate weight measurement is critical for recipe consistency and regulatory compliance. A small error can lead to product wastage or violations of safety standards.
In retail, load cells enhance the customer experience. They improve checkout accuracy and inventory management. Miscalculations at the point of sale can result in loss of revenue. A report indicated that 25% of retailers face challenges with inventory accuracy. This suggests there is room for improvement. By integrating load cells, businesses can create more efficient and reliable systems. Addressing these issues can lead to significant cost savings and improved customer trust.
What is a Load Cell Sensor and How Does it Work? - Key Applications of Load Cells in Industrial and Commercial Settings
| Application | Description | Load Cell Type | Typical Load Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Used for quality control and precise weight measurements on production lines. | Compression Load Cells | 0-2000 kg |
| Transportation | For monitoring vehicle load to ensure compliance with weight regulations. | Bending Beam Load Cells | 0-5000 kg |
| Food Industry | In scales for portion control and ingredient measurement. | Shear Beam Load Cells | 0-1500 kg |
| Construction | For monitoring load during structural testing and material handling. | Tension Load Cells | 0-10000 kg |
| Retail | Used in electronic scales for pricing based on weight. | Single Point Load Cells | 0-750 kg |
Understanding Load Cell Accuracy: Specifications and Calibration Standards
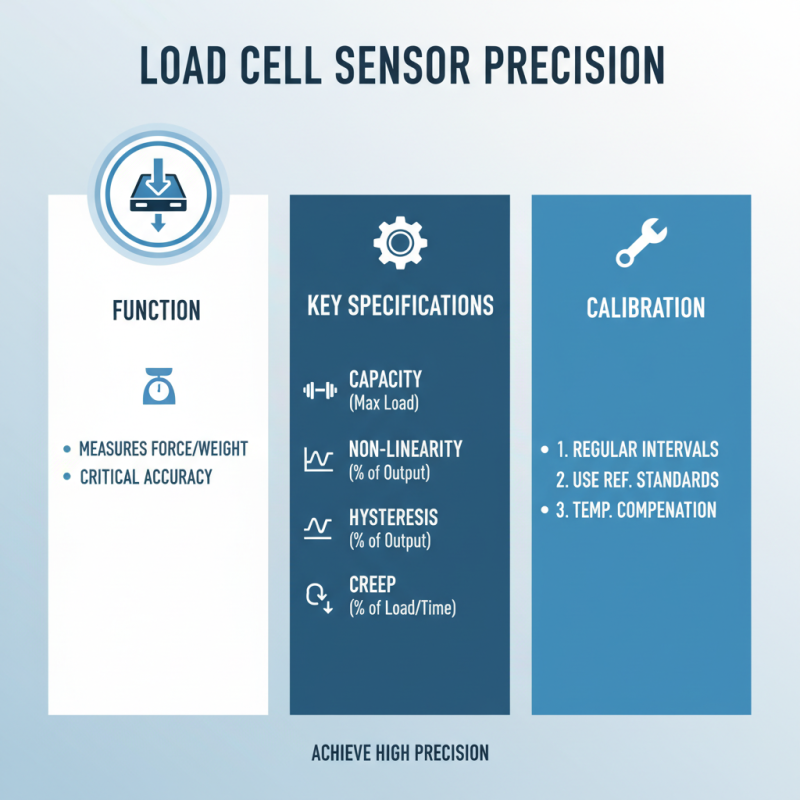
Load cell sensors measure force or weight. Their accuracy is critical in various applications. To achieve high precision, understanding specifications and calibration is vital.
When looking at accuracy, consider the sensor's capacity. It should align with its intended use. Calibration standards also play a crucial role. Regular calibration ensures the sensor provides reliable data. This is important for industries that rely on precise measurements.
**Tips:** Always check load cell specifications before purchase. Calibration should be done at regular intervals. Neglecting calibration can lead to errors. Remember, a small mistake in measurement can cause bigger issues down the line.
Related Posts
-

Top Load Cell Types and Their Applications in Industrial Weighing Systems
-

Best Tension Load Cell for Accurate Weight Measurement?
-
How to Choose Load Cell Sensors for Accurate Measurements?
-

2026 Top Tension Compression Load Cell Trends and Innovations?
-

5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Thin Load Cell
-

Understanding the Benefits of Through Hole Load Cell for Accurate Measurements

