 sales@loadcellsensor.com
sales@loadcellsensor.com

What is a Load Sensor and How Does it Work?
A Load Sensor plays a crucial role in various applications, from industrial machinery to consumer electronics. According to Dr. Samantha Lee, a prominent expert in sensor technology, "Load Sensors are vital for accurate measurements in modern engineering." These devices measure force or weight, translating the physical pressure into readable electrical signals.
The functionality of Load Sensors is intricate yet fascinating. They detect changes in resistance or capacitance, providing real-time data. Their use can be seen in smart scales, weight sensing for transportation, and even in robotic arms. However, many users misunderstand their calibration process. An improperly calibrated Load Sensor can lead to inaccurate readings.
Despite their significance, Load Sensors are not without challenges. Environmental factors can impact their performance. Temperature variations or sudden shocks may lead to errors. Understanding these limitations is essential for effective use in any field. The journey to mastering Load Sensors invites both innovation and reflection on its complexities.
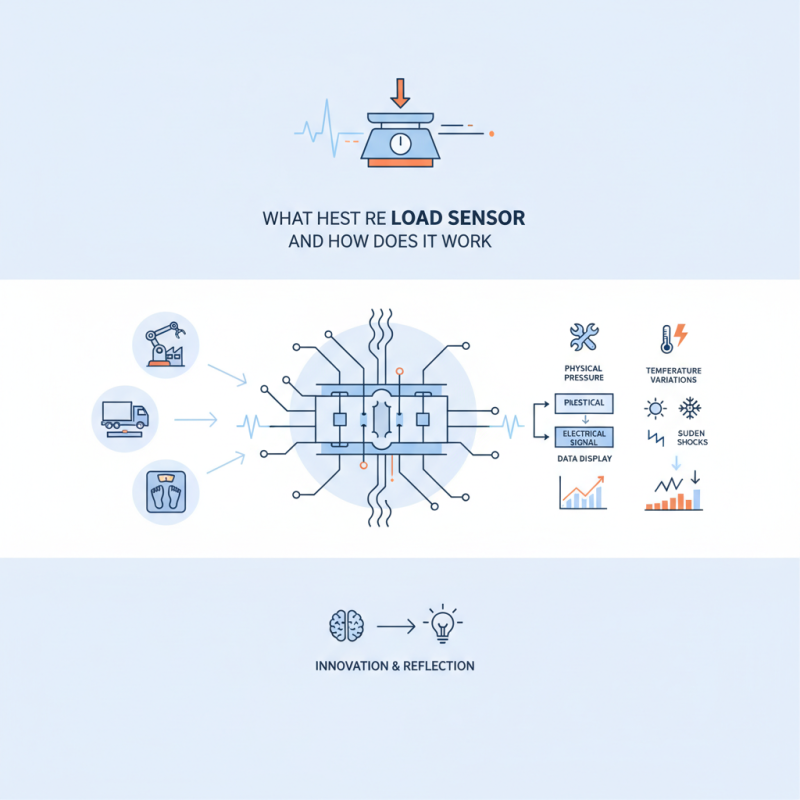
What is a Load Sensor?
Load sensors are essential devices used to measure weight or force. They convert mechanical force into measurable electrical signals. This is crucial for various applications in industries, from scales to robotics. The sensor's design often includes a strain gauge, which detects deformation under a load.
Tips: Consider the environment when choosing a load sensor. External factors like temperature and humidity can affect accuracy. Ensure proper calibration to maintain reliability.
Load sensors come in various configurations. S-beam, bending beam, and cylindrical are common types. Each type suits different applications. For instance, S-beam sensors are valuable in hanging scales, while bending beams are ideal for platform scales. Installing these sensors requires careful attention to alignment and mounting. Misalignment can lead to inaccurate readings.
Tips: Regular maintenance is vital. Dust and debris can disrupt performance. Check connections frequently for signs of wear. Understanding these details ensures optimal use. Load sensors are fascinating tools, but they require thoughtful implementation.
Key Components of Load Sensors
Load sensors play a crucial role in various applications. They are used to measure weight and load in many industries. Understanding their key components helps in selecting the right type for specific tasks.
One of the primary components is the strain gauge. This device detects deformation when weight is applied. It converts mechanical strain into electrical signals. Another important element is the load cell, which houses the strain gauge. It can come in various shapes, depending on the application. For instance, some are donut-shaped, while others are in cylindrical forms.
Signal conditioning circuitry is also vital. It amplifies and processes the signals from the load cell. Accurate measurements depend on this circuitry. Additionally, a power source is necessary to operate the sensor. Every component works together to provide reliable data. Engineers should consider each part carefully. Overlooking any component can lead to inaccuracies.
Types of Load Sensors and Their Applications
Load sensors are essential in various applications, providing crucial data about weight and force. Different types of load sensors are designed for unique purposes.
Strain gauge sensors are prevalent in industrial settings. They work by measuring the deformation of a material when weight is applied. These sensors are reliable and precise, making them suitable for quality control.
Another type is the piezoelectric sensor. This sensor generates an electric charge in response to mechanical stress. They excel in dynamic weight measurements. However, they may lack accuracy for static loads. These sensors are often used in applications like weighing pads for trucks or testing equipment.
Load cells, often used in elevators or shopping scales, represent another category. They convert weight into an electrical signal. This type is often employed in commercial weighing. It's important to note that every application can introduce challenges. For instance, overload can damage the sensor. Therefore, understanding load limits is crucial.
How Load Sensors Work: The Technical Process
Load sensors are critical for measuring weight and force. They detect and convert mechanical forces into measurable electrical signals. This process is essential in various applications, from industrial scales to robotics. Generally, load sensors use strain gauges to sense the deformation caused by the load. When a load is applied, the sensor deforms slightly. This deformation changes the electrical resistance, which can be measured.
The signals generated by load sensors can be quite small. Thus, they often require amplification for accurate readings. It’s important to calibrate load sensors properly to ensure accuracy. Even the best sensors can produce outliers if not managed well. Designers should consider environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and vibrations. These can affect sensor performance in unpredictable ways.
Tips: Always check for compatibility with existing systems. Test the setup in a controlled environment first. Regular maintenance can prevent unexpected failures. Being aware of potential sensor drift over time is crucial for reliability. Monitoring these factors can enhance the effectiveness of load sensors in real-world applications.
Factors Affecting Load Sensor Performance
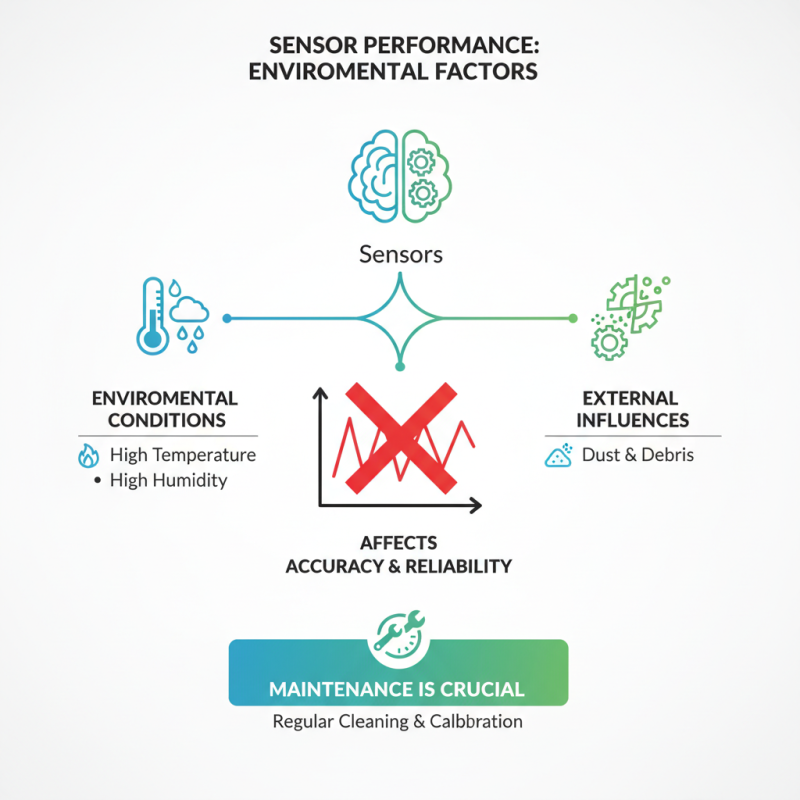
Load sensors play a crucial role in various applications, from industrial environments to everyday devices. However, several factors can influence their performance significantly. Environmental conditions are one key aspect. High temperatures or humidity may affect the sensor's accuracy. Additionally, dust or debris on the sensor can lead to incorrect readings. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure reliable performance.
Calibration is another significant factor. Load sensors must be properly calibrated for precise measurements. Miscalibration can result in repeated errors. Furthermore, the material used in the load cell affects its reaction to different loads. For instance, a material that is too rigid may not deform correctly, leading to inaccurate data.
Electrical noise can also disrupt load sensor performance. Power surges or fluctuations introduce inconsistencies in readings. Proper shielding and grounding are necessary to mitigate these issues. It’s important to remember that even the slightest oversight can lead to unexpected results. Ensuring optimal conditions is crucial for maintaining sensor integrity.
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Guide to Comparing the Top Weight Transducers for Global Buyers
-

5 Key Advantages of Choosing the Best Force Transducer for Your Applications
-

Top Strategies for Leveraging Force Transducer Technology in Global Procurement
-

Explore Cutting-Edge Weight Sensors at the Record-Breaking 137th Canton Fair!
-

Understanding the Key Technical Specifications of the Best Force Transducer and How to Choose the Right One
-

12 Expert Tips for Maximizing Efficiency with Compression Force Sensors

