 sales@loadcellsensor.com
sales@loadcellsensor.com

What is a Reaction Torque Sensor and How Does It Work?
In the realm of precision engineering and dynamic testing, the Reaction Torque Sensor plays a pivotal role in measuring torque in various applications. These sensors are designed to provide accurate and reliable feedback regarding the rotational forces acting on rotating machinery, thus ensuring optimal performance and safety in industrial environments. As Dr. Emily Johnson, a leading expert in torque measurement technology, states, "The Reaction Torque Sensor is essential for understanding the dynamics of mechanical systems and ensuring their efficient operation."
The functionality of a Reaction Torque Sensor is grounded in its ability to detect and measure the reactive forces produced during torque application. By employing advanced technology, these sensors can deliver real-time data, which is crucial for engineers and technicians working to optimize design and operational parameters. The insights gained from Reaction Torque Sensors are invaluable for a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, where precision and reliability are paramount.

Definition of Reaction Torque Sensor
A reaction torque sensor is a critical device used in various engineering applications to measure the torque acting on a rotating shaft or connection. This type of sensor operates based on the principle of converting mechanical forces into electrical signals, allowing precise monitoring and analysis of torque values in real-time. Often found in automotive testing, aerospace applications, and industrial machinery, reaction torque sensors play a vital role in ensuring operational efficiency and safety. According to a recent industry report by Research and Markets, the torque sensor market is expected to reach a valuation of over $500 million by 2025, driven by the surge in demand for torque measurement in various sectors.
The working mechanism of a reaction torque sensor involves the application of mechanical stress to a sensing element, typically a strain gauge or piezoelectric element, which then produces a corresponding electrical output. This output can be analyzed to evaluate the torque exerted on the sensor. Notably, these sensors are characterized by their high sensitivity and accuracy, with many models boasting a measurement range of 0-1000 Nm and an accuracy level of up to ±0.5%. The ability to provide real-time data enables engineers to optimize design processes and maintain equipment, significantly reducing the risk of mechanical failure and enhancing overall productivity.
What is a Reaction Torque Sensor and How Does It Work? - Definition of Reaction Torque Sensor
| Parameter | Description | Value/Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Torque Range | The maximum torque that can be measured | 0 - 500 Nm |
| Accuracy | The percentage of error in measurement | ±0.5% |
| Frequency Response | The sensor's ability to accurately measure changing torque | Up to 1000 Hz |
| Operating Temperature | Range of temperatures under which the sensor can operate | -20 to 85 °C |
| Sensor Type | Type of technology used in the sensor | Strain Gauge |
| Output Signal | The signal produced by the sensor for data transmission | Analog (0-10V) / Digital (RS232) |
| Weight | Weight of the sensor for installation considerations | 1.5 kg |
Principle of Operation for Reaction Torque Sensors
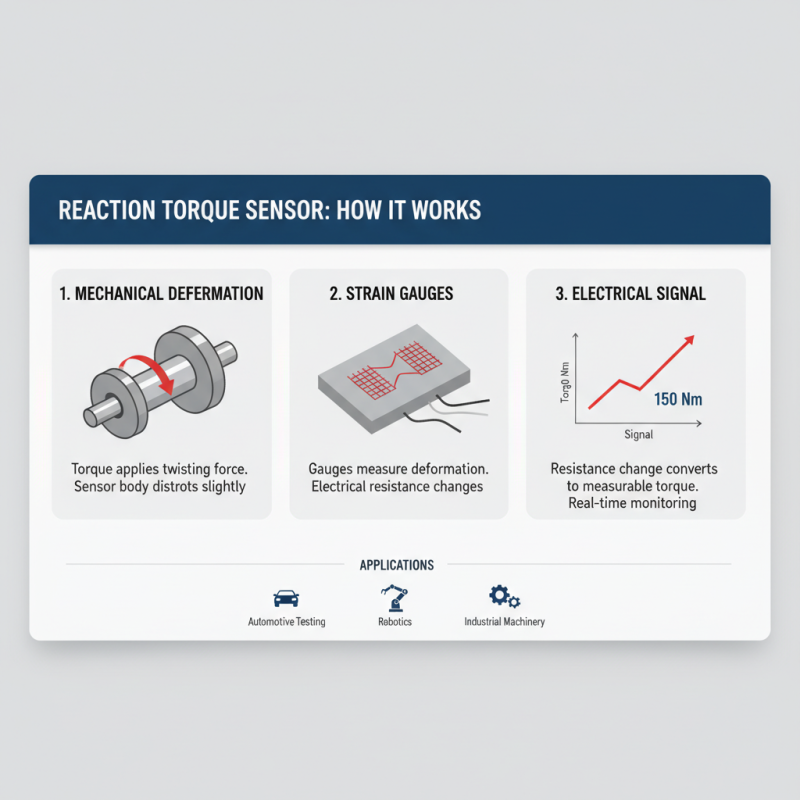
Reaction torque sensors are critical devices used to measure the twisting force or torque applied to a shaft without making any physical alterations to the system. The principle behind these sensors is based on mechanical deformation—in which the sensor’s structure can be distorted by the torque, resulting in a measurable electrical signal. Typically, these sensors utilize strain gauges that are strategically placed on the sensor's body. When torque is applied, these gauges undergo deformation, producing a change in resistance that can be correlated to the torque magnitude through precise calibration. This principle allows for real-time monitoring and analysis of torque in various applications, such as automotive testing, robotics, and industrial machinery.
In terms of performance metrics, reaction torque sensors are known for their high accuracy and reliability, with many devices achieving an accuracy rate of up to ±0.5% of the full scale. According to a report from Industry Research, the global torque sensor market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2020 to 2027, driven largely by advancements in sensing technology and an increasing demand for automation in industrial sectors. Additionally, reaction torque sensors offer advantages including compact design and high durability, making them suitable for environments where space is restrictive and operational life is critical. By integrating these sensors into machinery, industries can enhance operational efficiency and ensure safety standards by monitoring torque levels continuously.
Types of Reaction Torque Sensors and Their Applications
Reaction torque sensors are essential devices that measure the torque exerted by or on an object. They are widely used in various industries due to their versatility and precision. The two primary types of reaction torque sensors are rotary and static sensors. Rotary sensors are designed for applications involving rotational movements, measuring the torque in rotating shafts, and helping to ensure proper functionality in machinery such as motors and gearboxes. Conversely, static sensors are employed in environments where torque is applied without rotation, often utilized in assembling processes or equipment testing.
The applications of reaction torque sensors are vast and diverse. In automotive industries, they play a crucial role in testing engines and monitoring the performance of braking systems. In aerospace, these sensors are used for ensuring the integrity of components under high-stress conditions. Moreover, reaction torque sensors contribute significantly in robotics, where they help in calibrating movements to ensure the robots operate smoothly without overexertion or damage. Additionally, manufacturing and assembly lines utilize these sensors to guarantee that components are tightened to the specified torque, enhancing safety and reliability.
Advantages of Using Reaction Torque Sensors

Reaction torque sensors are vital components in various industries, offering precise measurement of torque generated by rotating objects. Their importance lies in their ability to provide accurate feedback, which is crucial for the optimization of mechanical systems. These sensors capture the torque being applied, enabling operators to make informed decisions about system performance and safety.
One of the significant advantages of using reaction torque sensors is their ability to enhance the accuracy of torque measurements. This leads to improved control in applications such as robotic systems, automotive testing, and industrial machinery. By ensuring precise torque application, manufacturers can reduce wear and tear on components, ultimately extending the lifespan of their equipment.
Tip: When selecting a reaction torque sensor, consider the torque range and sensitivity required for your specific application. This will ensure that you get optimal performance and accuracy from your sensor.
Another advantage is their contribution to safety in operational environments. By monitoring torque consistently, these sensors can trigger alerts if the applied torque exceeds predetermined thresholds, thereby preventing potential failures or accidents. This feature is crucial in high-stakes environments where machinery or operator safety can be compromised.
Tip: Regular calibration of your reaction torque sensor can significantly enhance its reliability and accuracy. Make it a part of your routine maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Installation and Calibration of Reaction Torque Sensors
Installation and calibration of reaction torque sensors are critical processes that ensure accurate and reliable measurements in various applications, such as automotive testing, machinery monitoring, and robotics. Proper installation involves securely mounting the sensor to the torque application point, ensuring that it is aligned accurately with the direction of the torque to be measured. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), misalignment during installation can lead to measurement errors exceeding 5%, highlighting the importance of precision in sensor positioning.
Once installed, calibration is the next essential step to validate the sensor's accuracy. This process typically involves applying known torque values and adjusting the sensor output to match these values within predefined tolerances. Industry standards, such as those stipulated by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), recommend calibration intervals based on the frequency of use and the operational conditions faced by the sensor. For example, torque sensors exposed to high-vibration environments may require more frequent calibration to maintain accuracy, whereas those in stable settings can usually adhere to annual or biennial calibration schedules. Maintaining stringent calibration protocols not only enhances data integrity but also assures compliance with regulatory requirements, ultimately leading to more reliable operational outcomes across various industries.
Torque Sensor Installation and Calibration Data
This bar chart illustrates the torque measurements before and after the calibration of reaction torque sensors. It indicates that the calibration process improved the measurement accuracy from 5 Nm to 10 Nm.
Related Posts
-

Unleashing China's Manufacturing Excellence: A Deep Dive into the Best Torque Sensor Innovations
-

Precision Engineering: Chinese Manufacturing Innovating Global Torque Transducer Solutions
-

Maximizing Precision: Key Techniques for Effective Torque Sensor Implementation
-

5 Compelling Reasons Why Torque Sensors Revolutionize Industrial Applications
-

Exploring Innovative Torque Sensor Types: Real-World Applications and Benefits
-

Understanding the Basics of Torque Sensor Functionality and Applications

