 sales@loadcellsensor.com
sales@loadcellsensor.com
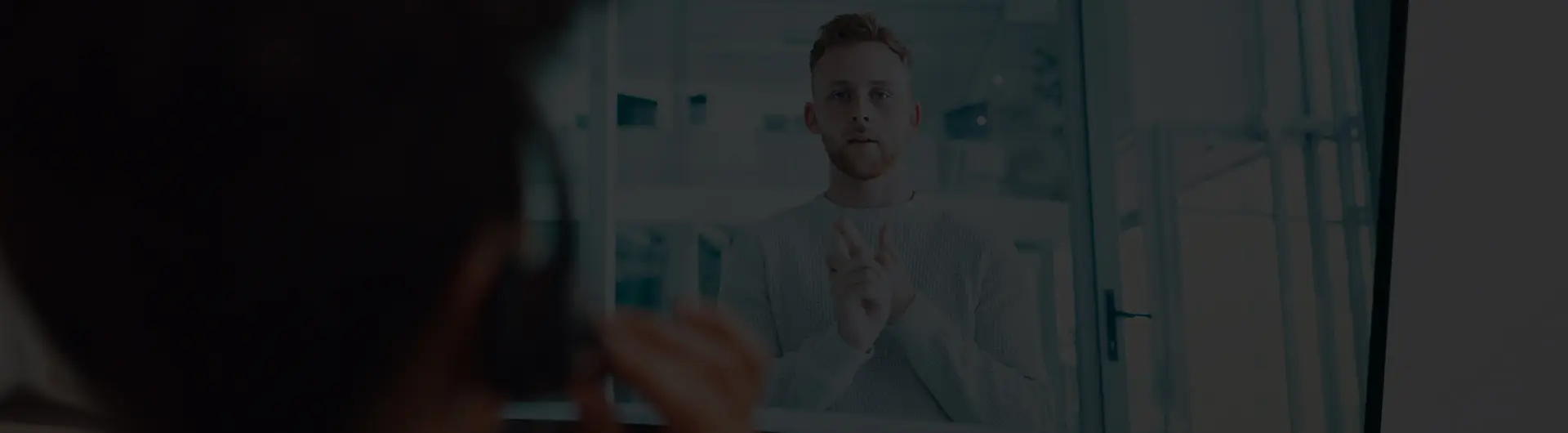

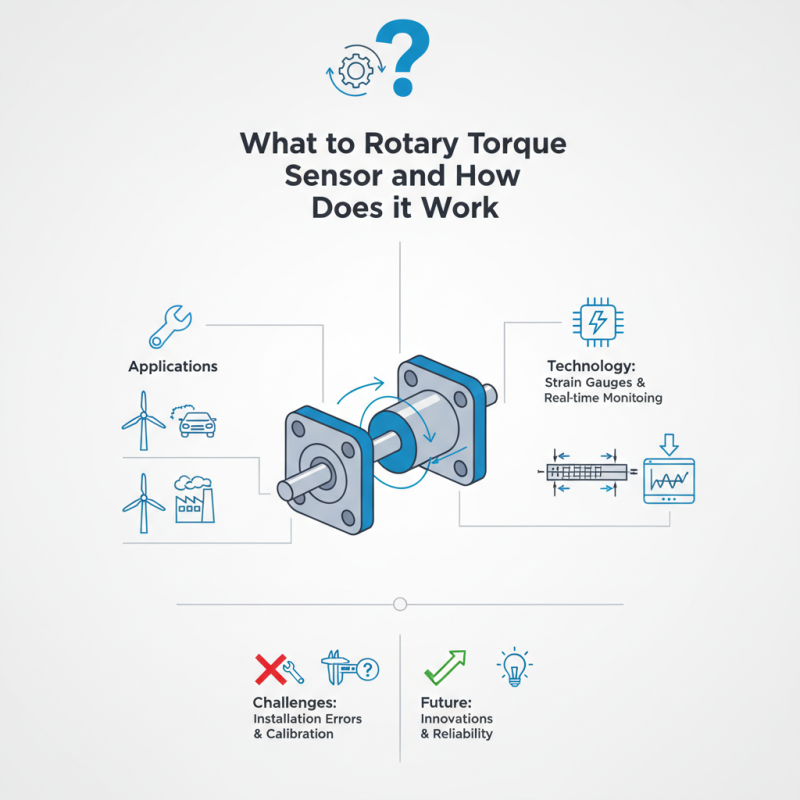
What is a Rotary Torque Sensor and How Does it Work?
A Rotary Torque Sensor is a crucial device in many industrial applications. It measures the torque applied to a rotating object, providing valuable data for engineers and technicians. These sensors are often used in automotive testing, manufacturing processes, and wind turbine operations.
The technology behind a Rotary Torque Sensor is fascinating. It typically uses strain gauges, which convert mechanical energy into electrical signals. This process allows for real-time monitoring of torque levels. Accurate measurements are essential for ensuring system performance and preventing failures.
However, there are challenges in using these sensors. Factors like installation errors and calibration issues can affect their accuracy. Understanding these nuances is crucial for leveraging the full potential of Rotary Torque Sensors. As technology evolves, clearer guidelines and innovations may enhance their reliability.
Understanding the Basics of Rotary Torque Sensors
A rotary torque sensor measures the torque applied to a rotating object. This technology is crucial in various applications, from automotive to industrial machinery. Understanding how these sensors work starts with grasping the basic components: a sensing element, signal conditioning, and an output interface.
The sensing element detects changes in torque. It often relies on strain gauges. When torque is applied, the strain gauges deform, producing an electrical signal. This signal is then amplified and processed by the signal conditioning unit. Finally, the data is sent to a display or control system for interpretation. These sensors can be mounted on motors, shafts, or other rotating equipment.
Tips for using rotary torque sensors effectively include regular calibration. This ensures accurate readings. Also, be mindful of the environment. Extreme temperatures can affect performance. Always refer to datasheets for specific operational limits. It's common for users to overlook these factors. Understanding your sensor's limits can save time and enhance reliability. Not every setup is perfect initially. Be open to adjustments for better accuracy.
Components of a Rotary Torque Sensor Explained
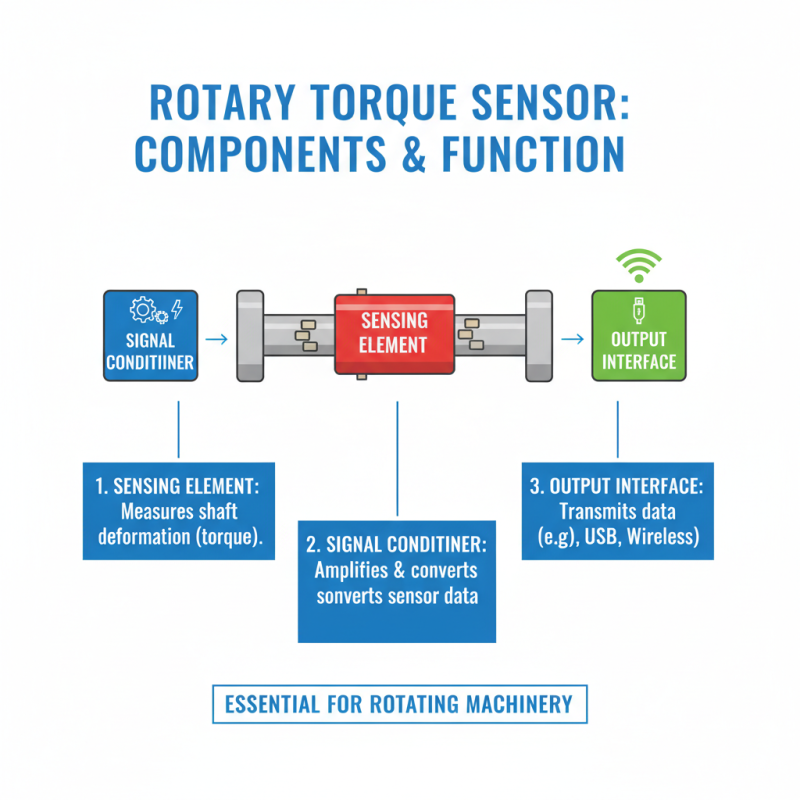
A rotary torque sensor is essential for measuring the torque applied to a rotating shaft. Understanding its components helps reveal how it functions. The primary parts include the sensing element, the signal conditioner, and the output interface.
The sensing element often consists of strain gauges. They detect deformation caused by torque. This small change in resistance translates into a torque measurement. Next, the signal conditioner amplifies these signals for better accuracy. It also filters noise, ensuring the data is clear and usable.
Lastly, the output interface communicates the information to a monitoring system. This is critical for real-time applications. However, there can be challenges. Calibration issues may arise, affecting accuracy. Sensor placement is also vital; incorrect positioning can lead to erroneous readings. Understanding these components allows for improved applications but also highlights areas for further optimization.
How Rotary Torque Sensors Measure Torque
Rotary torque sensors are crucial devices in various industries. They measure the torque applied in rotating systems. Understanding how they work is vital for efficiency and safety. These sensors typically use strain gauges or magnetostrictive technology to capture precise torque values.
When torque is applied to a rotating shaft, it deforms slightly. This deformation affects the resistance of the strain gauge, translating into an electrical signal. The readings then convert into torque measurements. The response time of these sensors is critical. A delay may happen if the sensor cannot keep up with fast rotations. This can impact system performance.
Calibration is essential in maintaining accuracy. Even minor miscalculations can lead to significant errors over time. Regular testing ensures the sensor functions correctly. The integration of these sensors into complex systems requires careful planning. They must handle varying loads and temperatures. Understanding these factors can improve the overall durability and reliability of the measurement system.
Applications of Rotary Torque Sensors in Various Industries
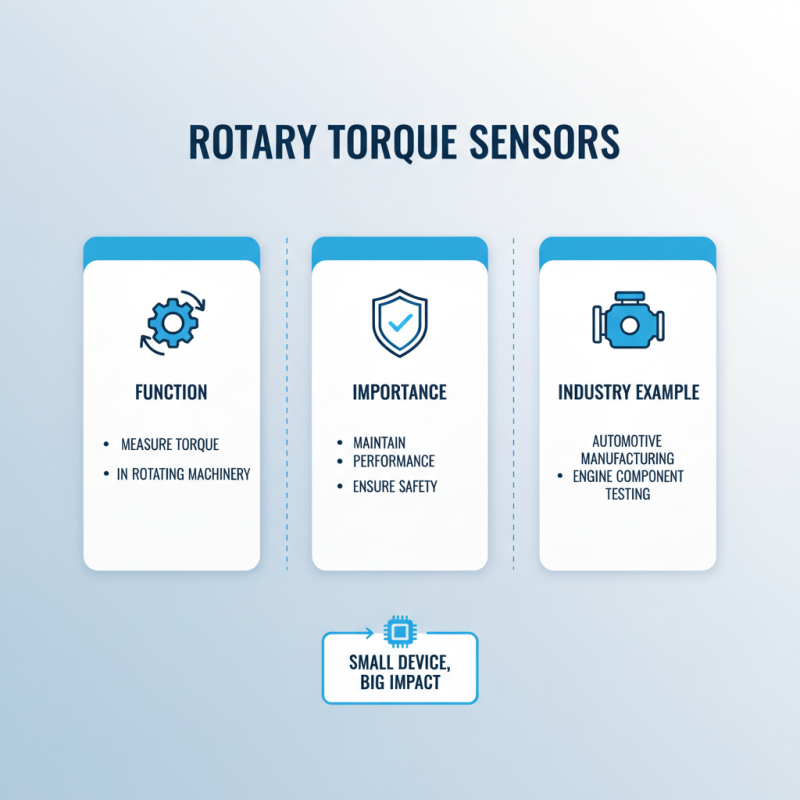
Rotary torque sensors are vital in various industries. They measure torque in rotating machinery. This measurement is crucial for maintaining performance and safety. For instance, in automotive manufacturing, these sensors help test engine components. They ensure that parts meet the required specifications. It’s fascinating to see how small devices influence large systems.
In aerospace, rotary torque sensors monitor critical operations. They help ensure that every rotation is precise. This data is essential for pilot safety. Engineers rely on this technology to avoid costly failures. However, there are challenges. Sensors can wear out, leading to inaccurate readings. Regular calibration is necessary.
**Tip:** Regularly inspect your torque sensors. This helps maintain accuracy over time. By doing this, you can catch issues early.
In robotics, these sensors play a key role. They assist in fine-tuning movements, allowing for precision tasks. But, there are drawbacks. Many sensors can be complex to install. A misunderstanding of their functions can lead to errors. Engineers must take time to understand the technology fully.
**Tip:** Provide training sessions for staff. Ensure everyone knows how to use sensors correctly. This can reduce mistakes and improve productivity.
Benefits and Limitations of Using Rotary Torque Sensors
Rotary torque sensors are vital in measuring rotational force in various applications. They offer significant advantages. For instance, they enhance precision in torque measurement. According to a market report, the global torque sensor market is projected to grow significantly, with a CAGR of about 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth highlights their increasing relevance in industries like automotive and manufacturing.
However, rotary torque sensors also have limitations. Their sensitivity to vibrations can skew results, leading to inaccuracies. Additionally, installation can be complex, requiring expert knowledge. A report indicated that about 30% of sensor inaccuracies stem from improper installation. Organizations should consider these factors to maximize their benefits.
Moreover, cost is a significant concern. High-quality rotary torque sensors can be expensive. Companies may hesitate to invest due to budget constraints. Despite these challenges, the benefits of improved efficiency and accuracy can outweigh the costs. Ultimately, understanding these limitations is crucial for effective implementation.
Torque Measurement Trends Using Rotary Torque Sensors
This bar chart illustrates the torque measurement trends in various applications over the last five years. It shows how the utilization of rotary torque sensors has increased in automotive, manufacturing, and robotics sectors, highlighting their growing importance in precise torque measurements.
Related Posts
-
Understanding the Importance of Shaft Torque Sensors in Modern Engineering Practices
-

What is a Reaction Torque Sensor and How Does It Work?
-

Unleashing China's Manufacturing Excellence: A Deep Dive into the Best Torque Sensor Innovations
-

Precision Engineering: Chinese Manufacturing Innovating Global Torque Transducer Solutions
-

How to Select the Best Rotary Torque Transducer for Your Industrial Needs
-

Maximizing Precision: Key Techniques for Effective Torque Sensor Implementation

